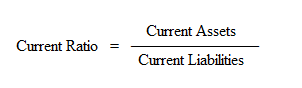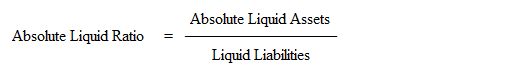I. Liquidity Ratios :
Liquidity Ratios measure the firms’ ability to pay off current dues i.e., repayable within a year. Liquidity ratios are otherwise called as Short Term Solvency Ratios. The important liquidity ratios are
1. Current Ratio
2. Liquid Ratio
3. Absolute Liquid Ratio
1. Current Ratio :
This ratio is used to assess the firm’s ability to meet its current liabilities. The relationship of current assets to current liabilities is known as current ratio. The ratio is calculated as:
Current Assets are those assets, which are easily convertible into cash within one year. This includes cash in hand, cash at bank,
sundry debtors, bills receivable, short term investment or marketable securities, stock and prepaid expenses.
Current Liabilities are those liabilities which are payable within one year. This includes bank overdraft, sundry creditors, bills payable and outstanding expenses.
Illustration :
From the following compute current ratio:
| Rs. | Rs. | ||
| Stock | 36,500 | Prepaid expenses | 1,000 |
| Sundry Debtors | 63,500 | Bank overdraft | 20,000 |
| Cash in hand & bank | 10,000 | Sundry creditors | 25,000 |
| Bills receivable | 9,000 | Bills payable | 16,000 |
| Short term investments | 30,000 | Outstanding expenses | 14,000 |
‘
Solution:
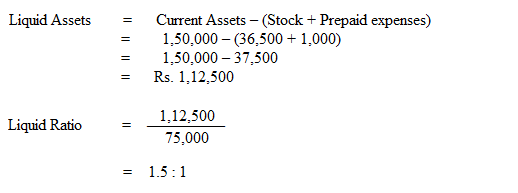
2. Liquid Ratio
This ratio is used to assess the firm’s short term liquidity. The relationship of liquid assets to current liabilities is known as liquid
ratio. It is otherwise called as Quick ratio or Acid Test ratio. The ratio is calculated as:
Liquid assets means current assets less stock and prepaid expenses.
Illustration :
Taking the figures from the above illustration liquid ratio is calculated as follows:
Solution:

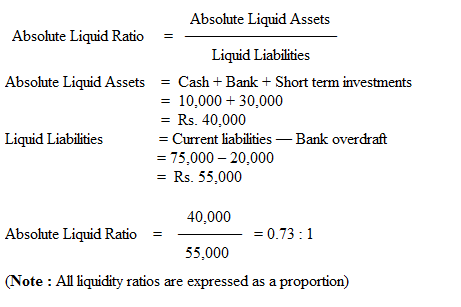
3. Absolute Liquid Ratio
It is a modified form of liquid ratio. The relationship of absolute liquid assets to liquid liabilities is known as absolute liquid ratio. This ratio is also called as ‘Super Quick Ratio’. The ratio is calculated as:
Absolute liquid assets means cash, bank and short term investments. Liquid liabilities means current liabilities less bank overdraft.
Illustration :
Taking the figures from Illustration : 1
Solution: