Integrated Communication Network for Banks Security and Control Systems :
Banks are exposed to many risks in their activities relating to management of funds on line banking services. credit card and other e- banking products/services are also facing risks which are associated with the use of IT tools, channels, platforms. Banks should have a good and effective control system to handle IT related issues and risks.
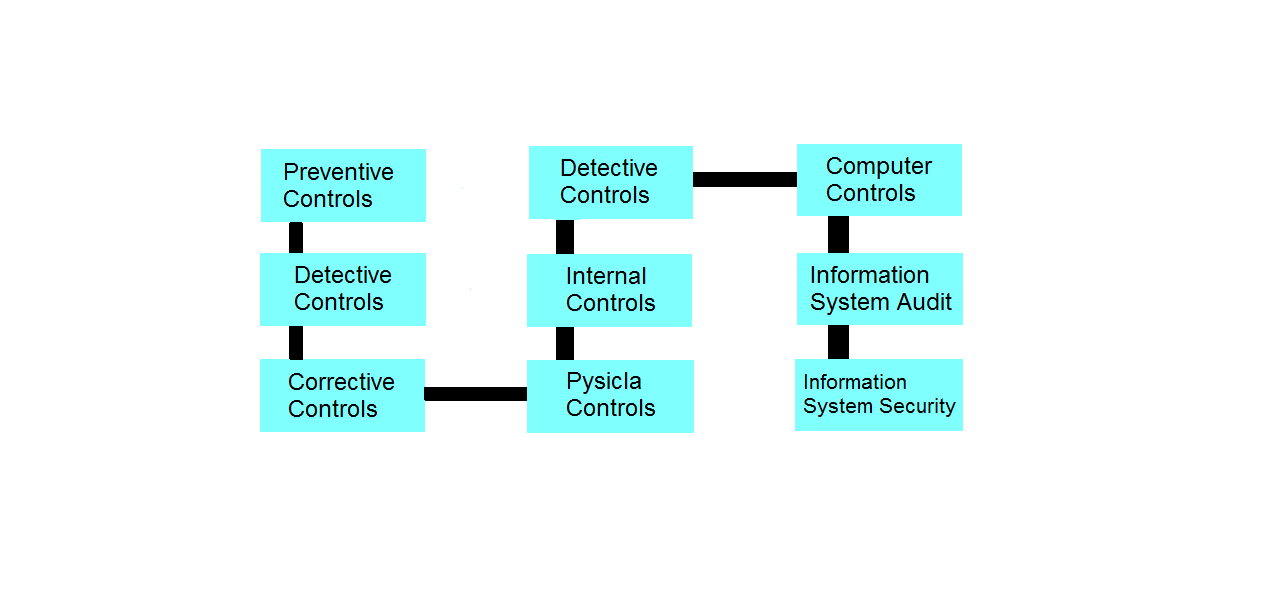
Control system can be classified as:
Preventive Controls: This type of control stops errors or irregularities. Good design/ screen lay out reduces or stops the errors at the time of coding data or entering data from source document.
Detective Controls: Identification of errors or irregularities happens after they occur. For example: An input validation program identifies data input errors.
Corrective Controls: These types of controls remove or reduce the effects of errors and irregularities after they have been identified. If any data is corrupted during transmission the communication software (with inbuilt control) may request for retransmission of information/data.
Physical Controls: In computerized environment, the control of access is very important in view of the confidential and sensitive information/data which are being processed/stored at the data processing center.
Access Control assist the organization and users in restricting entry to authorized persons only to the computer room and also allowing access to computer media, computer components, data, documentation etc. Unauthorized persons should not be allowed to undertake repairs/ maintenance of computer hardware. Access to the computer system should be protected through pass word protection mechanism. Access to the computer system can be allowed by means of PIN, biometric methodology. Access control should be very strict and only authorized users,
officers should be allowed inside the data center, computer room and all others should be allowed to enter the data center and computer rooms after recording in the access log.
Output controls: Hard copies of all important reports generated should be preserved properly as per the bank’s record maintenance policy.
As part of disaster management, the computer room, data centers need to be checked for proper functioning of fire extinguishers, smoke detectors and other devices. Backup tapes and other data should be stored in off sites. Regular checks should be carried out to ensure that such back up CDs and other tools/data can be used in case of an emergency/contingency.
Internal Controls: To ensure that the accounting data and other sensitive customer information are accurate and reliable and also to protect assets of the bank, a system of internal controls are built in the computerized systems. An effective and efficient internal control would assist the bank management to run the bank’s operations in a better controlled environment.
Accounting Controls may be in the form of (a) dual controls and authorizations (b) validation checks on data (c) other controls on access to the software applications.
Some other controls include validation of each transaction against limits and balances, stop payments, post dated and stale dated cheques, etc.
Operational Controls: Operational controls are embedded in software whereas access controls can be enforced by the system software and an application software at different levels. The operational controls are usually provided in the application software to ensure data integrity and processing. To ensure operational controls, some tools like audit trail, checksum and data encryption are used. Audit trail maintains a record of processes that update the data and information. Checksum is a number calculated on the basis of certain key information in the system. Checksum is generated to ensure data integrity stored in a computer file. Data Encryption is the process of systematic encoding of data before transmission to protect the system from unauthorized access, and an unauthorized person cannot decipher it. End to end encryption protects the integrity of data passing between a sender and receiver. In the electronic funds transfer systems, a control mechanism which applies a message authentication code is used to identify changes to a message in transit.
Computer Audit covers, review of operations to ensure compliances of bank’s systems and procedures and policies, standards.
It includes review of the system’s integrity covering fraud detection/prevention, application program and operating system, user acceptance tests at the time of software program implementation and up gradation.
Audit around the computer: The auditor examines the internal control system of the computer installation and related input and output of the application system. ‘Around the computer audit’ needs to be carried out to ensure/ verify: (i) the systems are supported by well tested software (ii) a clear cut system generated audit trail is available (iii) proper physical controls are in place (iv) duties and responsibilities of various employees are well defined and segregated.
Audit through the computer: This is used to check whether logic and controls are available within the system and records produced by the system are in conformity with the input and expected level of output. Audit through the computers can be carried out by test checks, mock trial runs, and the tools like special audit modules embedded in the application systems to generate audit evidence. Auditors also use audit software consisting of computer program as audit tool. Computer Aided Audit Tools and Techniques (CAATTs) are used to audit computer generated files, records, data and documents. This tool also assists for evaluation of the internal controls of computerized environment in banks.
Information System Audit (IS): This audit is carried out through the IT systems with the assistance of CAATTs and CMITTs. These tools are used to carry out the information system audit. The information system audit covers various controls like preventive, detective and corrective controls and their effectiveness in protecting bank’s information systems. Information System audit assesses the strengths and weaknesses of the bank’s information system. It identifies the risks of exposure associated with the existing computerized environment. The audit findings can be used as a preventive tool by the banks to take appropriate action to mitigate such risks. IS of a bank can also highlight the following:
– integrity of the system to safeguard the assets of the bank
– reveals the status of the information system indicating any short comings as well
– assists banks to take a better decision on the management control system of the bank