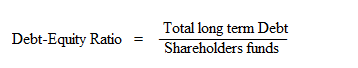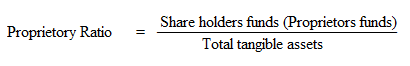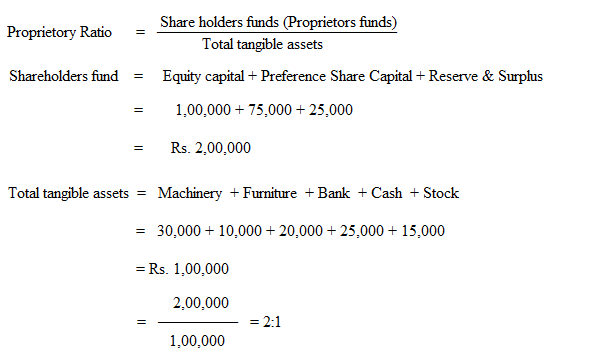Solvency Ratios
Solvency refers to the firms ability to meet its long term indebtedness. Solvency ratio studies the firms ability to meet its long term obligations. The following are the important solvency ratios:
1. Debt-Equity Ratio
2. Proprietory Ratio
1. Debt Equity Ratio
This ratio helps to ascertain the soundness of the long term financial position of the concern. It indicates the proportion between total long term debt and shareholders funds. This also indicates the extent to which the firm depends upon outsiders for its existence. The ratio is calculated as:
Total long term debt includes Debentures, long term loans from banks and financial institutions. Shareholders funds includes Equity share capital, Preference share capital, Reserves and surplus.
Illustration :
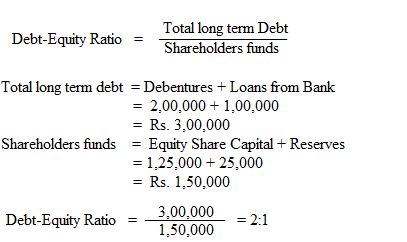
Calculate Debt Equity Ratio from the following information.
Rs.
Debentures 2,00,000
Loan from Banks 1,00,000
Equity share capital 1,25,000
Reserves 25,000
Solution:
2. Proprietory Ratio
This ratio shows the relationship between proprietors or shareholders funds and total tangible assets. The ratio is calculated as:
Illustration :
From the following calculate Proprietory Ratio
| Rs. | Rs. | ||
| Equity share capital | 1,00,000 | Furniture | 10,000 |
| Preference share capital | 75,000 | Bank | 20,000 |
| Reserves & surplus | 25,000 | Cash | 25,000 |
| Machinery | 30,000 | Stock | 15,000 |
| Goodwill | 5,000 |
(Note : All solvency ratios are expressed as a proportion.)