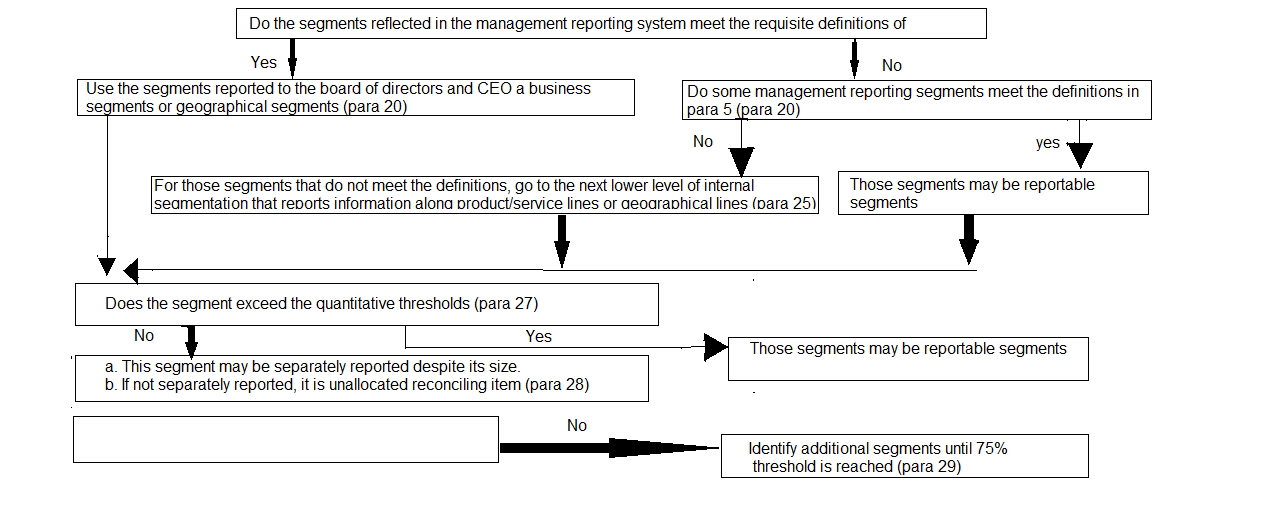
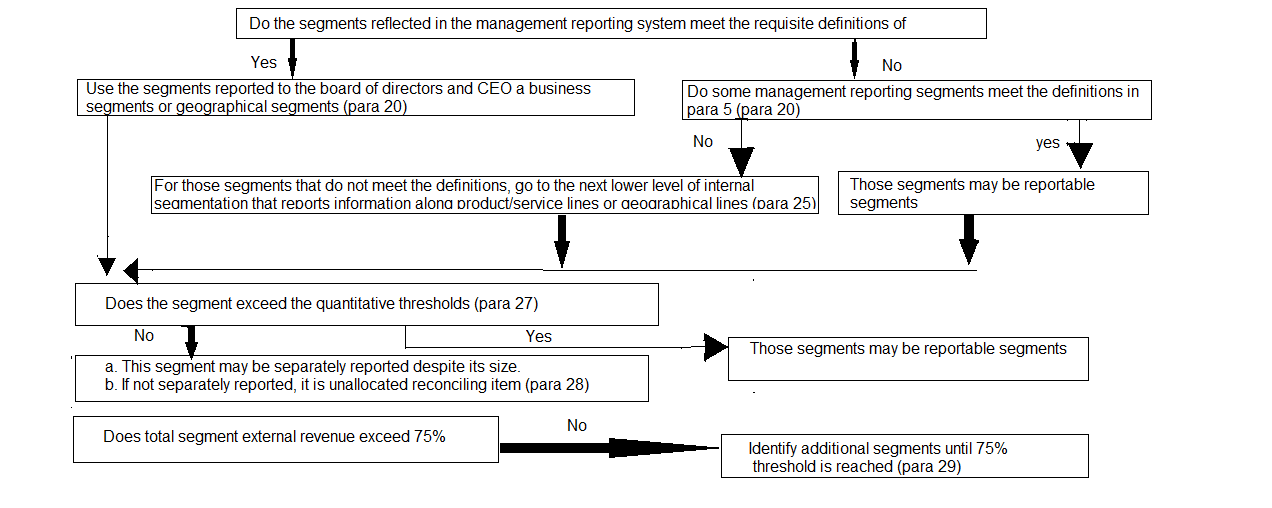
Illustration I
Segment Definition Decision Tree
The purpose of this illustration is to illustrate the application of paragraphs 24-32 of the Accounting Standard.
Illustration II
Illustration on Determination of Reportable Segments [Paragraphs 27-29]
This illustration does not form part of the Accounting Standard. Its purpose is to illustrate the application of paragraphs 27-29 of the Accounting Standard.
An enterprise operates through eight segments, namely, A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H. The relevant information about these segments is given in the following table (amounts in Rs.’000):
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | Total (Segments) | Total (Enterprise) | |
| 1. SEGMENT REVENUE
(a) External Sales |
– | 255 | 15 | 10 | 15 | 50 | 20 | 35 | 400 | |
| (b) Inter-segment Sales | 100 | 60 | 30 | 5 | – | – | 5 | – | 200 | |
| (c) Total Revenue | 100 | 315 | 45 | 15 | 15 | 50 | 25 | 35 | 600 | 400 |
| 2. Total Revenue of each segment as a percentage oftotal revenue of all segments | 16.7 | 52.5 | 7.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 8.3 | 4.2 | 5.8 | ||
| 3. SEGMENT RESULT [Profit/(Loss)] | ||||||||||
| 4. Combined Result of all Segments in profits | 5 | 15 | 8 | 5 | 7 | 40 | ||||
| 5. Combined Result of all Segments in loss | (90) | (5) | (5) | (100) | ||||||
| 6. Segment Result as a percentage of the greater of the totals arrived at 4 and 5 above in absolute amount (i.e., 100) | 5 | 90 | 15 | 5 | 8 | 5 | 5 | 7 | ||
| 7. SEGMENT ASSETS | 15 | 47 | 5 | 11 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 9 | 100 | |
| 8. Segment assets as a percentage of total assets of all segments | 15 | 47 | 5 | 11 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 9 |
The reportable segments of the enterprise will be identified as below:
(a) In accordance with paragraph 27(a), segments whose total revenue from external sales and inter-segment sales is 10% or more of the total revenue of all segments, external and internal, should be identified a reportable segments. Therefore, Segments A and B are reportable segments.
(b) As per the requirements of paragraph 27(b), it is to be first identified whether the combined result of all segments in profit or the combined result of all segments in loss is greater in absolute amount. From the table, it is evident that combined result in loss (i.e., Rs.100,000) is greater. Therefore, the individual segment result as a percentage of Rs.100,000 needs to be examined. In accordance with paragraph 27(b), Segments B and C are reportable segments as their segment result is more than the threshold limit of 10%.
(c) Segments A, B and D are reportable segments as per paragraph 27(c), as their segment assets are more than 10% of the total segment assets.
Thus, Segments A, B, C and D are reportable segments in terms of the criteria laid down in paragraph 27.
Paragraph 28 of the Standard gives an option to the management of the enterprise to designate any segment as reportable segment. In the given case, it is presumed that the management decides to designate Segment E as a reportable segment.
Paragraph 29 requires that if total external revenue attributable to reportable segments identified as aforesaid constitutes less than 75% of the total enterprise revenue, additional segments should be identified as reportable segments even if they do not meet the 10% thresholds in paragraph 27, until at least 75% of total enterprise revenue is included in reportable segments.
The total external revenue of Segments A, B, C, D and E, identified above as reportable segments, is Rs.295,000. This is less than 75% of total enterprise revenue of Rs.400,000. The management of the enterprise is required to designate any one or more of the remaining segments as reportable segment(s) so that the external revenue of reportable segments is at least 75% of the total enterprise revenue. Suppose, the management designates Segment H for this purpose. Now the external revenue of reportable segments is more than 75% of the total enterprise revenue.
Segments A, B, C, D, E and H are reportable segments. Segments F and G will be shown as reconciling items.
Illustration III
Illustrative Segment Disclosures
This illustration does not form part of the Accounting Standard. Its purpose is to illustrate the application of paragraphs 38-59 of the Accounting Standard.
This illustration illustrates the segment disclosures that this Standard would require for a diversified multi-locational business enterprise. This example is intentionally complex to illustrate most of the provisions of this Standard.
INFORMATION ABOUT BUSINESS SEGMENTS (NOTE xx)
(All amounts in Rs. lakhs)
| Paper Products | Office Products | Publishing | Other Operations | Eliminations | Consolidated Total | |||||||
| Current Year |
Previous Year |
Current Year |
Previous Year |
Current Year |
Previous Year |
Current Year |
Previous Year |
Current Year |
Previous Year |
Current Year |
Previous Year |
|
| REVENUE | ||||||||||||
| External sales | 55 | 50 | 20 | 17 | 19 | 16 | 7 | 7 | ||||
| Inter- segment sales | 15 | 10 | 10 | 14 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | (29) | (30) | ||
| Total Revenue | 70 | 60 | 30 | 31 | 21 | 20 | 9 | 9 | (29) | (30) | 101 | 90 |
| Paper Products | Office Products | Publishing | Other Operations | Eliminations | Consolidated Total | |||||||
| Current Year |
Previous Year |
Current Year |
Previous Year |
Current Year |
Previous Year |
Current Year |
Previous Year |
Current Year |
Previous Year |
Current Year |
Previous Year |
|
| RESULT | ||||||||||||
| Segment result | 20 | 17 | 9 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | (1) | (1) | 30 | 24 |
| Unallocated corporate expenses | (7) | (9) | ||||||||||
| Operating profit | 23 | 15 | ||||||||||
| Interest expense | (4) | (4) | ||||||||||
| Interest income |
2 | 3 | ||||||||||
| Income taxes | (7) | (4) | ||||||||||
| Profit from ordinary activities | 14 | 10 | ||||||||||
| Paper Products | Office Products | Publishing | Other Operations | Eliminations | Consolidated Total | |||||||
| Current Year |
Previous Year |
Current Year |
Previous Year |
Current Year |
Previous Year |
Current Year |
Previous Year |
Current Year |
Previous Year |
Current Year |
Previous Year |
|
| Extraord- inary loss: uninsured earthquake damage to factory | (3) | (3) | ||||||||||
| Net profit | 14 | 7 | ||||||||||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||||||||||||
| Segment assets | 54 | 50 | 34 | 30 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 9 | 108 | 99 | ||
| Unallocated corporate assets | 67 | 56 | ||||||||||
| Total assets | 175 | 155 | ||||||||||
| Segment liabilities | 25 | 15 | 8 | 11 | 8 | 8 | 1 | 1 | 42 | 35 | ||
| Paper Products | Office Products | Publishing | Other Operations | Eliminations | Consolidated Total | |||||||
| Current Year |
Previous Year |
Current Year |
Previous Year |
Current Year |
Previous Year |
Current Year |
Previous Year |
Current Year |
Previous Year |
Current Year |
Previous Year |
|
| Unallocated corporate liabilities | 40 | 55 | ||||||||||
| Total liabilities | 82 | 90 | ||||||||||
| Capital expenditure | 12 | 10 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 3 | |||||
| Depre- ciation |
9 | 7 | 9 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 4 | ||||
| Non-cash expenses other than depre-
ciation |
8 | 2 | 7 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | ||||
Note xx-Business and Geographical Segments (amounts in Rs. lakhs)
Business segments: For management purposes, the Company is organised on a worldwide basis into three major operating divisions-paper products, office products and publishing — each headed by a senior vice president. The divisions are the basis on which the company reports its primary segment information. The paper products segment produces a broad range of writing and publishing papers and newsprint. The office products segment manufactures labels, binders, pens, and markers and also distributes office products made by others. The publishing segment develops and sells books in the fields of taxation, law and accounting. Other operations include development of computer software for standard and specialised business applications. Financial information about business segments is presented in the above table (from page 314 to page 317).
Geographical segments: Although the Company’s major operating divisions are managed on a worldwide basis, hey operate in four principal geographical areas of the world. In India, its home country, the Company produces and sells a broad range of papers and office products. Additionally, all of the Company’s publishing and computer software development operations are conducted in India. In the European Union, the Company operates paper and office products manufacturing facilities and sales offices in the following countries: France, Belgium, Germany and the U.K. Operations in Canada and the United States are essentially similar and consist of manufacturing papers and newsprint that are sold entirely within those two countries. Operations in Indonesia include the production of paper pulp and the manufacture of writing and publishing papers and office products, almost all of which is sold outside Indonesia, both to other segments of the company and to external customers.
Sales by market: The following table shows the distribution of the Company’s consolidated sales by geographical market, regardless of where the goods were produced:
Sales Revenue by
Geographical Market
Current Year Previous Year
India 19 22
European Union 30 31
| Canada and the United States | 28 | 21 |
| Mexico and South America | 6 | 2 |
| Southeast Asia (principally Japan and Taiwan) | 18 | 14 |
| 101 | 90 |
Assets and additions to tangible and intangible fixed assets by geographical area: The following table shows the carrying amount of segment assets and additions to tangible and intangible fixed assets by geographical area in which the assets are located:
Carrying Additions to
Amount of Fixed Assets
Segment Assets and
Intangible
Assets
| Current Year |
Previous Year |
Current Year |
Previous Year |
|
| India | 72 | 78 | 8 | 5 |
| European Union | 47 | 37 | 5 | 4 |
| Canada and the United States | 34 | 20 | 4 | 3 |
| Indonesia | 22 | 20 | 7 | 6 |
| 175 | 155 | 24 | 18 |
Assets and additions to tangible and intangible fixed assets by geographical area: The following table shows the carrying amount of segment assets and additions to tangible and intangible fixed assets by geographical area in which the assets are located:
Carrying Additions to
Amount of Fixed Assets
Segment Assets and
Intangible
Assets
| Current Year |
Previous Year |
Current Year |
Previous Year |
|
| India | 72 | 78 | 8 | 5 |
| European Union | 47 | 37 | 5 | 4 |
| Canada and the United States | 34 | 20 | 4 | 3 |
| Indonesia | 22 | 20 | 7 | 6 |
| 175 | 155 | 24 | 18 |
Segment revenue and expense: In India, paper and office products are manufactured in combined facilities and are sold by a combined sales force. Joint revenues and expenses are allocated to the two business segments on a reasonable basis. All other segment revenue and expense are directly attributable to the segments.
Segment assets and liabilities: Segment assets include all operating assets used by a segment and consist principally of operating cash, debtors, inventories and fixed assets, net of allowances and provisions which are reported as direct offsets in the balance sheet. While most such assets can be directly attributed to individual segments, the carrying amount of certain assets used jointly by two or more segments is allocated to the segments on a reasonable basis. Segment liabilities include all operating liabilities and consist principally of creditors and accrued liabilities. Segment assets and liabilities do not include deferred income taxes.
Inter-segment transfers: Segment revenue, segment expenses and segment result include transfers between business segments and between geographical segments. Such transfers are accounted for at competitive market prices charged to unaffiliated customers for similar goods. Those transfers are eliminated in consolidation.
Unusual item: Sales of office products to external customers in the current year were adversely affected by a lengthy strike of transportation workers in India, which interrupted product shipments for approximately four months. The Company estimates that sales of office products during the four-month period were approximately half of what they would otherwise have been.
Extraordinary loss: As more fully discussed in Note x, the Company incurred an uninsured loss of Rs.3,00,000 caused by earthquake damage to a paper mill in India during the previous year.
Illustration IV
Summary of Required Disclosure
This illustration does not form part of the Accounting Standard. Its purpose is to summarise the disclosures required by paragraphs 38-59 for each of the three possible primary segment reporting formats.
Figures in parentheses refer to paragraph numbers of the relevant paragraphs in the text.
| PRIMARY FORMAT IS BUSINESS SEGMENTS | PRIMARY FORMAT IS GEOGRAPHICAL SEGMENTS BY LOCATION OF ASSETS | PRIMARY FORMAT IS GEOGRAPHICAL SEGMENTS BY LOCATION OF CUSTOMERS |
| Required Primary Disclosures | Required Primary Disclosures | Required Primary Disclosures |
| Revenue from external customers by business segment [40(a)] | Revenue from external customers by location of assets [40(a)] | Revenue from external customers by location of customers [40(a)] |
| Revenue from transactions with other segments by business segment [40(a)] | Revenue from transactions with other segments by location of assets [40(a)] | Revenue from transactions with other segments by location of customers [40(a)] |
| Segment result by business segment [40(b)] | Segment result by location of assets [40(b)] | Segment result by location of customers [40(b)] |
| Carrying amount of segment assets by business segment [40(c)] | Carrying amount of segment assets by location of assets [40(c)] | Carrying amount of segment assets by location of customers [40(c)] |
| Segment liabilities by business segment [40(d)] | Segment liabilities by location of assets
[40(d)] |
Segment liabilities by location of customers [40(d)] |
| Cost to acquire tangible and intangible fixed assets by business segment [40(e)] | Cost to acquire tangible and intangible fixed assets by location of assets [40(e)] | Cost to acquire tangible and intangible fixed
assets by location of customers [40(e)]
|
| PRIMARY FORMAT IS BUSINESS SEGMENTS | PRIMARY FORMAT IS GEOGRAPHICAL SEGMENTS BY LOCATION OF ASSETS | PRIMARY FORMAT IS GEOGRAPHICAL SEGMENTS BY LOCATION OF CUSTOMERS |
| Required Primary Disclosures | Required Primary Disclosures | Required Primary Disclosures |
| Depreciation and amortisation expense by business segment [40(f)] | Depreciation and amortisation expense by location of assets[40(f)] | Depreciation and amortisation expense by location of
customers[40(f)] |
| Non-cash expenses other than depreciation and amortisation by business segment [40(g)] | Non-cash expenses
other than depreciation and amortisation by location of assets [40(g)] |
Non-cash expenses
other than depreciation and amortisation by location of customers [40(g)] |
| Reconciliation of revenue, result, assets, and liabilities by business segment [46] | Reconciliation of revenue, result, assets, and liabilities [46] | Reconciliation of revenue, result, assets, and liabilities [46] |
| Required Secondary Disclosures | Required Secondary Disclosures | Required Secondary Disclosures |
| Revenue from external customers by location of customers [48] | Revenue from external customers by business segment [49] | Revenue from external customers by business segment [49] |
| Carrying amount of segment assets by location of assets [48] | Carrying amount of segment assets by business segment [49] | Carrying amount of segment assets by business segment [49] |
| Cost to acquire tangible and intangible fixed assets by location of assets [48] | Cost to acquire tangible and intangible fixed assets by business segment [49] | Cost to acquire tangible and intangible fixed
assets by business segment [49] |
| Revenue from external customers by geographical customers if different from
location of assets [50] |
| PRIMARY FORMAT IS BUSINESS SEGMENTS | PRIMARY FORMAT IS GEOGRAPHICAL SEGMENTS BY LOCATION OF ASSETS | PRIMARY FORMAT IS GEOGRAPHICAL SEGMENTS BY LOCATION OF CUSTOMERS |
| Required Secondary Disclosures | Required Secondary Disclosures | Required Secondary Disclosures |
| Carrying amount of segment assets by location of assets if different from location of customers [51] | ||
| Cost to acquire tangible and intangible fixed
assets by location of assets if different from location of customers [51] |
||
| Other Required Disclosures | Other Required Disclosures | Other Required Disclosures |
| Basis of pricing inter- segment transfers and any change therein [53] | Basis of pricing inter- segment transfers and any change therein [53] | Basis of pricing inter-segment transfers and any change therein [53] |
| Changes in segment accounting policies [54] | Changes in segment accounting policies [54] | Changes in segment accounting policies [54] |
| Types of products and services in each
business segment [58] |
Types of products and services in each
business segment [58] |
Types of products and services in each
business segment [58] |
| Composition of each geographical segment [58] | Composition of each geographical segment [58] | Composition of each geographical segment [58] |