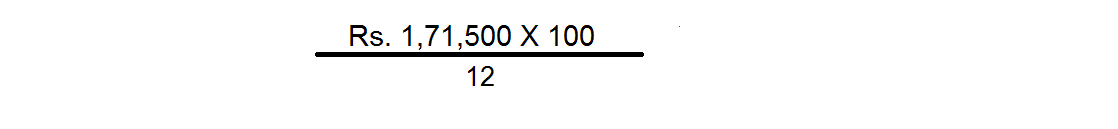Methods of Valuing Goodwill :
There are basically two methods of valuing goodwill: (i) Simple profit method; (ii) Super profit method.
(i) Simple Profit Method
Goodwill is sometimes valued on the basis of a certain number of years’ purchase of the average profits of the past few years. While calculating average profits for the purposes of valuation of goodwill certain adjustments are made. Some of them are the following:
(a) All actual expenses and losses not likely to occur in the future are added back to profits;
(b) Expenses and losses expected to be borne in future are deducted from such profits;
(c) All profits likely to come in the future are added; and
(d) Even actual profits not likely to recur are deducted.
After having adjusted profit in the light of future possibilities, average profits are estimated and then the value of goodwill is estimated i.e., the average profits are ascertained and then the average is multiplied by a particular number, representing the number of years’ purchase. If goodwill is to be valued at 3 years’ purchase of the average profits which come to ` 20,000, the goodwill will be ` 60,000, i.e., 3 x ` 20,000.
This method has nothing to recommend itself since goodwill is attached to profits over and above what one can earn by starting a new business and not to total profits. It ignores the amount of capital employed for earning the profit. However, it is usual to adopt this method for valuing the goodwill of the practice of a professional person such as a chartered accountant or a doctor.
(ii) Super Profit Method
In this case the future maintainable profits of the firm are compared with the normal profits for the firm. Normal earnings of a business can be judged only in the light of normal rate of earning and capital employed in the business. However, this method of valuing goodwill would require the following informations:
1. A normal rate of return for representative firms in the industry.
2. The fair value of capital employed.
3. Estimated future maintainable profit.
Example: In the Illustration No. 1 given above, suppose the investors are satisfied with 12% return, then normal profit will be ` 7,56,000 i.e. 12% of ` 63,00,000. The future maintainable profit being ` 9,27,500, super profit will be ` 1,71,500. There are three methods of calculating goodwill based on super profit which are as under:
(a) (i) Purchase of Super Profit Method
Goodwill as per this method is: Super profit x A certain number of years. Under this method, an important point to note is that the number of years of purchase as goodwill will differ from industry to industry and from firm to firm. Theoretically, the number of years is to be determined with reference to the probability of a new business catching up with an old business. Suppose it is estimated that in four years’ time a business, if started de novo, will be earning about the same profits as an old business is earning now, goodwill will be equivalent to four times the super profits. In the example given above, goodwill will be ` 6,86,000 i.e., 4 x ` 1,71,500.
(ii) Sliding Scale Valuation of Super Profit
This method is a variation of the purchase method. This has been advocated by A.E. Cutforth and is based upon the theory that the greater the amount of super profit, the more difficult it would be to maintain. In this method the super profit is divided into two or three divisions. Each of these is multiplied by a different number of years’ purchase, in descending order from the first division. For example, if super profit is estimated at ` 2,25,000, goodwill be calculated as follows:
`
FirstRs.75,000 say 5 years 3,75,000
SecondRs.75,000 say 4 years 3,00,000
Third Rs. 75,000 say 3 years 2,25,000
Total goodwill 9,00,000
(b) Annuity Method of Super Profit
Goodwill as per this method is: Super profit x Annuity of Re. 1 at the normal rate of return for the stated number of years. Goodwill in this case is the discounted value of the total amount calculated as per purchase method. The idea behind super profit method is that the amount paid for goodwill will be recouped during the coming few years. But in this case, there is a heavy loss of interest. Hence, properly speaking what should be paid now is only the present value of super profits paid annually at the proper rate of interest. Tables show that the present value @ 12% of Re. 1 received annually for four years is 3.037. In the above illustration, the value of goodwill under this method will be ` 5,20,845 i.e. 3.037 x 1,71,500.
(c) Capitalisation of Super Profit
In this method the amount of super profit is capitalised at the normal rate of return. In other words, this method tries to find out the amount of capital needed for earning the super profit. The formula is: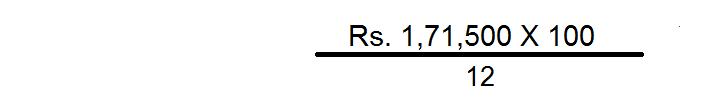
In the example given above, the value of goodwill will be Rs.14,29,167 i.e.
There is also another method of capitalisation frequently used. Under this method adjusted average profits are capitalised on the basis of normal rate of return and from such a value, the net assets of the business are substracted to arrive at the value of goodwill.
In the illustration given above, the value of total business will be Rs. 77,29,167 or say Rs.77,29,200. Therefore goodwill will be 14,29,200, i.e. Rs.77,29,200 less ` 63,00,000.
This method puts a very large value on goodwill. Really it is useful only when the future maintainable profit is less than the normal profit. It then determines the proper value of the firm.
Suppose the total net tangible assets of a company is ` 50 lakhs; the normal rate of return in the concerned industry is 14%; and the company earns a profit of ` 8,40,000. The total value of the business will be Rs.60 lakhs, i.e. 8,40,000 X 100/14
There is naturally no goodwill since the actual profit is less than the normal profit. However, it will be improper to pay Rs. 50 lakhs for the business since then the earning will not be 14%. The proper value of the business is Rs. 45 lakhs.
Illustration :
A Ltd. proposed to purchase the business carried on by M/s. X & Co. Goodwill for this purpose is agreed to be valued at three years’ purchase of the weighted average profits of the past four years. The appropriate weights to be used are:
2010-11 1 2012-13 3
2011-12 2 2013-14 4
The profit for these years are: 2010-11 – Rs. 1,01,000; 2011-12 – Rs.1,24,000; 2012-13- Rs. 1,00,000 and 2013-14 – Rs. 1,40,000.
On a scrutiny of the accounts the following matters are revealed:
(i) On 1st December, 2012 a major repair was made in respect of the plant incurring Rs. 30,000 which was charged to revenue. The said sum is agreed to be capitalised for goodwill calculation subject to adjustment of depreciation of 10% p.a. on reducing balance method.
(ii) The closing stock for the year 2011-12 was overvalued by Rs. 12,000.
(iii) To cover management cost an annual charge of ` 24,000 should be made for the purpose of goodwill valuation.
Compute the value of goodwill of the firm.
Solution:
Calculation of Adjusted Profits Rs. Rs.
| Profits – 2010-11 | 1,01,000 | |
| Less: Management expenses | 24,000 | |
| Adjusted Profits – 2010-11 | 77,000 | |
| Profits – 2011-12 | 1,24,000 | |
| Less: Over-valuation of closing stock | 12,000 | |
| Management expenses | 24,000 | 36,000 |
| Adjusted Profits – 2011-12 | 88,000 | |
| Profits – 2012-13 | 1,00,000 | |
| Add: Over-valuation of opening stock | 12,000 | |
| Major repairs of plant to be treated | ||
| as capital expenditure | 30,000 | 42,000 |
| 1,42,000 | ||
| Less: Depreciation on capital expenditure | ||
| @ 10% p.a. for 4 months from | ||
| December 1, 2012 to March 31, 2013 | ||
|
30,000 x 10 x 4 100 x 12 |
1000 1,41,000 |
|
| Less: Management expenses | 24,000 | |
| Adjusted Profits – 2012-13 | 1,17,000 | |
| Profits – 2013-14 | 1,40,000 | |
| Less: 10% Depreciation on ` 29,000 (block value | ||
| ` 30,000 – ` 1,000 – capital expenditure) | 2,900 | |
| 1,37,100 | ||
| Less: Management expenses | 24,000 | |
| Adjusted Profits – 2012-13 | 1,13,100 | |
Calculation of Average Profits
|
Year ended 31 March |
Profits
Rs. |
Weight
Rs. |
Product Rs. |
| 2010-11 | 77,000 | 1 | 77,000 |
| 2011-12 | 88,000 | 2 | 1,76,000 |
| 2012-13 | 1,17,000 | 3 | 3,51,000 |
| 2013-14 | 1,13,100 | 4 | 4,52,400 |
| 10 | 10,56,400 |
Average Profits = 10,56,400 – 10 = 1,05,640
Goodwill at three years’ purchase = Rs.1,05,640 x 3 = Rs.3,16,920
Illustration :
From the following information ascertain the value to goodwill of X Ltd. under super profit method.
Balance Sheet as on 31st March, 2014
| Liabilities | Rs. | assets | Rs. |
| Paid-up capital: | Goodwill at cost | 50,000 | |
| 5,000, shares of ` 100 each | Land and buildings | ||
| fully paid | 5,00,000 | at cost | 2,20,000 |
| Bank overdraft | 1,16,700 | Plant and machinery | |
| Sundry creditors | 1,81,000 | at cost | 2,00,000 |
| Provision for taxation | 39,000 | Stock in trade | 3,00,000 |
| Profit and loss appropriation | Book debts less | ||
| Account | 1,13,300 | provision for bad debts | 1,80,000 |
| 9,50,000 | 9,50,000 |
The company commenced operations in 2008 with a paid-up capital of ` 5,00,000. Profits for recent years (after taxation) have been as follows:
| Year ended 31st March ` |
| 2010 40,000 (loss) |
| 2011 88,000 |
| 2012 1,03,000 |
| 2013 1,16,000 |
| 2014 1,30,000 |
The loss in 2010 occurred due to a prolonged strike.
The income-tax paid so far has been at the average rate of 40%, but it is likely to be 50% from April 2013 onwards. Dividends were distributed at the rate of 10% on the paid up capital in 2011 and 2012 and at the rate of 15% in 2013 and 2014. The market price of shares is ruling at ` 125 at the end of the year ended 31st March, 2013. Profits till 2013 have been ascertained after debiting ` 40,000 as remuneration to the director. The company has approved a remuneration of ` 60,000 with effect from 1st April, 2013. The company has been able to secure a contract at an advantageous price thereby it can save materials worth ` 40,000 per annum for the next five years.
Solution:
Valuation of Goodwill of X Ltd.
| (i) Capital employed: | Rs. | |
| Land and building at cost | 2,20,000 | |
| Plant and machinery at cost | 2,00,000 | |
| Stock in trade | 3,00,000 | |
| Sundry debtors | 1,80,000 | |
| 9,00,000 | ||
| Less: Sundry liabilities: | ||
| Bank overdraft | 1,16,700 | |
| Sundry creditors | 1,81,000 | |
| Provision for taxation | 39,000 | 3,36,700 |
| Capital employed at the end of the year | 5,63,300 | |
| Add back | ||
| Dividend paid for the year | 75,000 | |
| Less: Half of the profits | 65,000 | 10,000 |
| Average capital employed | 5,73,300 |
(ii) Normal Rate of Return:
Average dividends for the last 4 years 12.5%Market price of shares on 31st March Rs.125
Normal rate of return:
Note: It may be more appropriate to relate the normal rate of return to the dividend paid in the last two years since price is related to dividend expected in future and, for that, the most recent experience is relevant.
In that case the normal rate of return will be 15×100/ 125 = 12%
(iii) Normal Profit on Average Capital employed:
@ 10% on Rs.5,73,300 57,330
@ 12% on Rs.5,73,300 68,796
(iv) Future Maintainable Profits – Weighted Average:
Year ended 31st March Profits Weight Product
2011 88,000 1 88,000
2012 1,03,000 2 2,06,000
2013 1,16,000 3 3,48,000
2014 1,30,000 4 5,20,000
10 11,62,000
Average annual profit (after tax) 1,16,200
Average annual profit (before tax) 1,16,200 x 100/60 1,93,667
Adjustments :
(i) Increase in remuneration – 20,000
(ii) Saving in cost of materials +40,000 20,000
2,13,667
Less: Taxation @ 50% 1,06,833
Future maintainable profit 1,06,834
(v) Super Profits
| Normal Rate 12% | Normal Rate 10% | |
| Average maintainable profits | 1,06,834 | 1,06,834 |
| Normal profit on capital employed | 68,796 | 57,330 |
| Super profit | 38,038 | 49,504 |
| Goodwill at 5 years’ purchase | ||
| of super profits | 1,90,190 | 2,47,520 |
| Goodwill at 3 years’ purchase | 1,14,114 | 1,48,512 |
Note: Three to five years’ purchase of super profits can be taken as fair value of goodwill. Thus, depending on the assumptions regarding the normal rate of return and the number of years’ purchase, goodwill may range between Rs. 1,14,114 and Rs. 2,47,520.