Rule 9 – Place of provision of specified services :
The place of provision of the specified services shall be the location of the service provider.
Specified services are as follows:-
(a) Services provided by a banking company, or a financial institution, or a non-banking financial company, to account holders;
(b) Online information and database access or retrieval services;
(c) Intermediary services;
(d) Service consisting of hiring of all means of transport other than, –
(i) aircrafts, and
(ii) vessels except yachts,
upto a period of one month.
Analysis of the rule
Specified services in rule 9 are as follows:-
(a) Banking services provided to account holders: Banking services provided to persons other than account holders will be covered under the main rule-rule 3.
Example of services provided by a banking company/financial institution etc. to account holders in the normal course of business:-
(i) Services linked to or requiring opening and operation of bank accounts such as lending, deposits, safe deposit locker etc.
(ii) Transfer of money including telegraphic transfer, mail transfer, electronic transfer etc.
Financial leasing services including equipment leasing and hire-purchase, merchant banking services, asset management services, advisory and other auxiliary financial services are few instances of the services that are generally NOT provided by a banking company or financial institution to an account holder in the ordinary course of business.
| 1. Account means an account bearing interest to the depositor, and includes a non-resident external account and a non-resident ordinary account [Rule 2(b)].
2. Banking company has the meaning assigned to it in section 45A(a) of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934 [Rule 2(c)]. Refer Chapter 6 of this Module for detailed explanation. 3. Financial institution has the meaning assigned to it in section 45-I(c) of the 4. Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934 [Rule 2(e)]. Refer Chapter 6 of this Module for detailed explanation. 4. Non-banking financial company means- (i) a financial institution which is a company; or (ii) a non-banking institution which is a company and which has as its principal business the receiving of deposits, under any scheme or arrangement or in any other manner, or lending in any manner; or (iii) such other non-banking institution or class of such institutions, as the Reserve Bank of India may, with the previous approval of the Central Government and by notification in the Official Gazette specify [Rule 2(k)]. |
(b) Online information and database access or retrieval services: As per rule 2(l), “online information and database access or retrieval services” means providing data or information, retrievable or otherwise, to any person, in electronic form through a computer network.
1. These services must be delivered over the internet or an electronic network which relies on the internet or similar network for their provision.
2. They should be completely automated, and require minimal human intervention.
3. Examples of these services are:-
- Web-based services providing access or download of digital content
- digitized content of books and other electronic publications
- online news, flight information and weather reports.
4. Sale or purchase of goods, articles etc over the internet, repair of software, or of hardware through the internet from a remote location, telecommunication services provided over the internet etc. shall not be included in the said services.
(c) Intermediary: As per rule 2(f), intermediary means a broker, an agent or any other person, by whatever name called, who arranges or facilitates a provision of a service (hereinafter called the main „service) or a supply of goods, between two or more pers ons, but does not include a person who provides the main service or supplies the goods on his account.
Accordingly, intermediary of goods, such as a commission agent or consignment agent are also included and a person who provides the main service or supplies the goods on his own account is excluded.
(i) Guiding principles to determine whether a person is an intermediary or not
In order to determine whether a person is acting as an intermediary or not, the following factors need to be considered:-
1. An intermediary cannot alter the nature or value of the service, the supply of which he facilitates on behalf of his principal, although the principal may authorize the intermediary to negotiate a different price.
2. The value of an intermediary‟s service is invariably identifiable from the main supply of service that he is arranging.
3. The service provided by the intermediary on behalf of the principal is clearly identifiable.
(ii) Services qualifying as „intermediary services‟
Services provided by the following persons will qualify as “intermediary services‟:-
(i) Travel Agent (any mode of travel)
(ii) Tour Operator
(iii) Commission agent (for service or goods)
(iv) Recovery Agent
Any other service wherever a provider of any service acts as an intermediary for another person, as identified by the guiding principles outlined above.
Inward remittances from abroad to beneficiaries in India through MTSOs: The remittances of money from overseas through the Money Transfer Service Operator (MTSO) route involves the following sequence of transactions:
Step 1: Remitter located outside India (say ‘A’) approaches a MTSO/bank (say B) located outside India for remitting the money to a beneficiary in India; ‘B’ charges a fee from ‘A’.
Step 2: ‘B’ avails the services of an Indian entity (agent) (say ‘C’) for delivery of money to the ultimate recipient of money in India (say ‘E’); ‘C’ is paid a commission/fee by ‘B’.
Step 3: ‘C’ may avail service of a sub-agent (D). ‘D’ charges fee/commission from ‘C’.
Step 4: ‘C’ or ‘D’, as the case may be, delivers the money to ‘E’ and may charge a fee from ‘E’.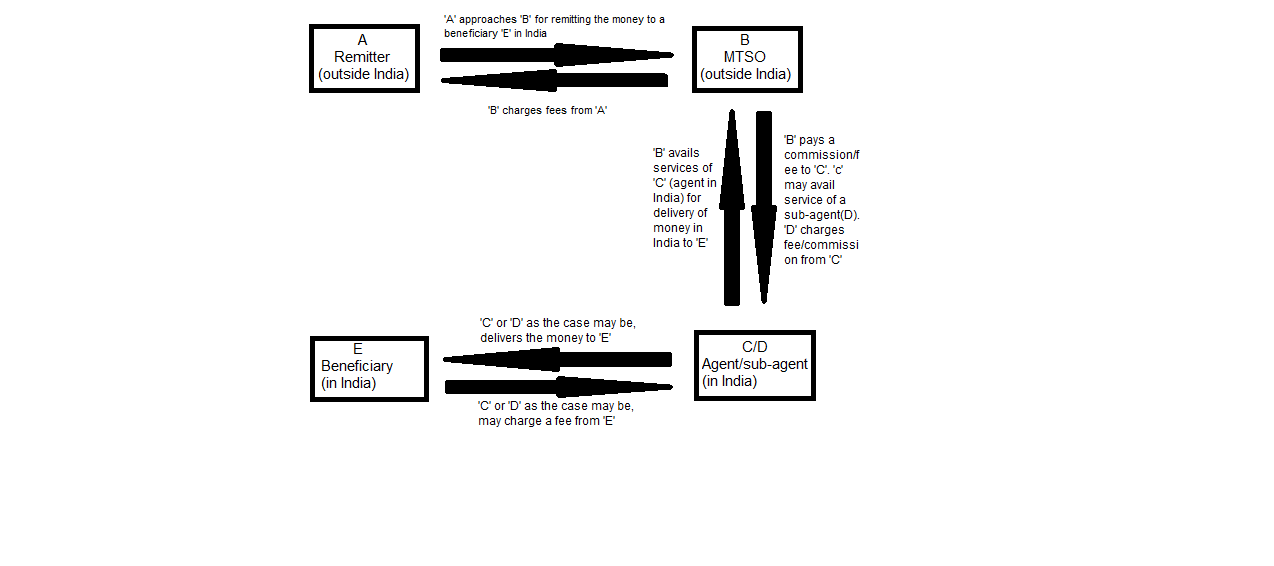
Circular No.180/06/2014 ST dated 14.10.2014 has clarified following issues in this regard:
| S. No | Issues | Clarification |
| 1 | Whether service tax is payable on remittance received in India from abroad? | No service tax is payable per se on the amount of foreign currency remitted to India from overseas. As the remittance comprises money, it does not in itself constitute any service in terms of the definition of ‘service’ [Section 65B(44)]. |
| 2 | Whether the service of an agent or the representation service provided by an Indian entity/ bank to a foreign MTSO in relation to money transfer falls in the category of intermediary service? | Yes. The Indian bank or other entity acting as an agent to MTSO in relation to money transfer, facilitates in the delivery of the remittance to the beneficiary in India. In performing this service, the Indian Bank/entity facilitates the provision of money transfer service by the MTSO to a beneficiary in India. For their service, agent receives commission or fee. Hence, the agent falls in the category of intermediary as defined in rule 2(f) of the Place of Provision of Service Rules, 2012. |
| 3 | Whether service tax is leviable on the service provided, as mentioned in point 2 above, by an intermediary/ agent located in India (in taxable territory) to MTSOs located outside India? | Service provided by an intermediary is covered by rule 9(c) of the Place of Provision of Service Rules, 2012. As per this rule, the place of provision of service is the location of service provider. Hence, service provided by an agent, located in India (in taxable territory), to MTSO is liable to service tax.
The value of intermediary service provided by the agent to MTSO is the commission or fee or any similar amount, by whatever name called, received by it from MTSO and service tax is payable on such commission or fee. |
| 4 | Whether service tax would apply on the amount charged separately, if any, by the Indian bank/entity/agent/sub-agent from the person who receives remittance in the taxable territory, for the service provided by such Indian bank/entity/agent/sub-agent. | Yes. As the service is provided by Indian bank/entity/agent/sub-agent to a person located in taxable territory, the place of provision is in the taxable territory. Therefore, service tax is payable on amount charged separately, if any. |
| 5 | Whether service tax would apply on the services provided by way of currency conversion by a bank /entity located in India (in the taxable territory) to the recipient of remittance in India? | Any activity of money changing comprises an independent taxable activity. Therefore, service tax applies on currency conversion in such cases in terms of the Service Tax (Determination of Value) Rules. Service provider has an option to pay service tax at prescribed rates in terms of Rule 6(7B) of the Service Tax Rules 1994. |
| 6 | Whether services provided by sub-agents to such Indian Bank/entity located in the taxable territory in relation to money transfer is leviable to service tax? | Sub-agents also fall in the category of intermediary. Therefore, service tax is payable on commission received by sub-agents from Indian bank/entity. |
(d) Service consisting of hiring of all means of transport other than aircrafts and vessels (except yacht), upto a period of one month: Following will constitute means of transport:-
- Land vehicles such as motorcars, buses, trucks;
- Vehicles designed specifically for the transport of sick or injured persons;
- Mechanically or electronically propelled invalid carriages;
- Trailers, semi-trailers and railway wagons.
The following are not “means of transport‟ for the purpose of clause (d) of this rule:-
- Aircrafts
- Vessels (except yacht)
- Racing cars;
- Containers used to store or carry goods while being transported;
- Dredgers, or the like.
Means of transport means any conveyance designed to transport goods or persons from one place to another [Rule 2(j)].
Hiring of vessels or aircraft, whether for upto one month or more, will be covered by the general rule 3, i.e., the location of the service receiver. Hiring of yachts would, however, be governed by rule 9(d) i.e., in case of hiring of yachts upto one month, the place of provision of service would be the location of service provider.
The above can also be understood with the help of the following example:
| Service consisting of hiring of – | Place of provision of service | ||
| Location of service provider | Location of service receiver | ||
| (i) | Aircraft up to a period of 20 days | ü | |
| (ii) | Aircraft up to a period of 90 days | ü | |
| (iii) | Vessel up to a period of 20 days | ü | |
| (iv) | Vessel up to a period of 90 days | ü | |
| (v) | Yachts up to a period of 20 days | ü | |
| (vi) | Yachts up to a period of 90 days | ü | |
| (vii) | Trucks up to a period of 20 days | ü | |
| (viii) | Trucks up to a period of 90 days | ü | |