Tax Dedution Analysis
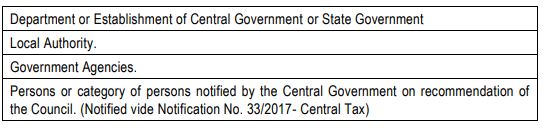
CGST Act vide Section 2 (53) defines the term Government to mean the Central Government. Section 51 (1), ibid refers to TDS related mandating by ‘Government’ (Central/State Government). Such mandating shall be for the following persons –
1. The above ‘persons’ are referred to as deductors.
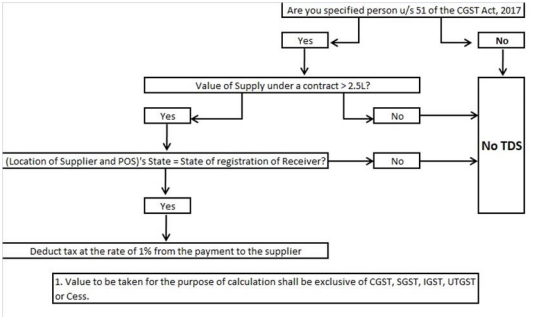
2. The deductors have to deduct tax at the rate of 1% from the payment made or credited to the supplier of taxable goods and / or services, notified by the Central Government or State Government on the recommendations of the Council. Deduction is required where the total value of supply under ‘a contract’ exceeds INR 2.5 lakhs. Value of supply shall exclude the tax indicated in the invoice. No deduction shall be made if the location of the supplier and the place of supply is in a State or Union territory which is different from the State or as the case may be, Union territory of registration of the recipient
3. The amount deducted shall be paid to the Central Government within ten days after the end of the month in which such deduction is made. Sub Rule 9 of rule 87 of the CGST rules provides) that payment shall be made by debiting the electronic cash ledger and crediting the electronic tax liability register.
4. As per Rule 66, the deductor shall furnish a TDS certificate in Form GSTR-7A to the deductee mentioning therein the following:
(a) contract value
(b) rate of deduction
(c) Amount deducted
(d) Amount paid to the appropriate Government
(e) Any other particulars as may be prescribed
5. This certificate has to be furnished within five days of remittance as mentioned above.
6. Certificate not furnished by the deductor: – If the deductor does not furnish the certificate of deduction-cum- remittance within five days of the remittance, the deductor has to pay a late fee of INR 100 per day from the 6th day until the day he furnishes the certificate. The maximum late fee is prescribed as INR 5000.
7. Non-remittance by the deductor: If the deductor does not remit the amount deducted as TDS, he is liable to pay penal interest under Section 50 in addition to the amount of tax deducted.
8. The amount of tax deducted reflected in Electronic Cash Ledger of deductee in the return in Form GSTR-7 filed by deductor shall be claimed as credit.
This provision enables the Government to cross-check whether the amount deducted by the deductor is correct and that there is no mis-match between the amount reflected in the Electronic Cash Ledger as reflected in the return filed by deductor. One may draw easy analogy from existing practice in income tax related E-TDS returns filed by deductor and 26AS statement available for viewing the TDS remitted in respect of his transactions by deductee.
9. Refund on excess collection: The deductor or the deductee can claim refund of excess deduction or erroneous deduction. The provisions of section 54 relating to refunds would apply in such cases. However, if the amount deducted has been credited to the Electronic Cash Ledger of the deductee, the deductor cannot claim refund (only deductee can claim).
10. As mentioned above, UTGST Act 2017, subject to its own provisions, adopts the provisions in CGST Act in respect of Tax Deduction at Source mutatis mutandis (Ref: Sec 21 of UTGST Act).
Issues and Concerns
None